In today’s digital age, where high-speed internet is essential for activities ranging from work and communication to entertainment and gaming, latency plays a key role in determining the quality of online experiences. While download and upload speeds are often the focus when discussing internet performance, latency—the delay before data is transferred—can be just as critical, particularly for real-time activities like gaming, video calls, and cloud-based collaboration.
This article delves into what internet latency is, the factors contributing to it, how it impacts various online activities, and ways to reduce it for a smoother online experience.
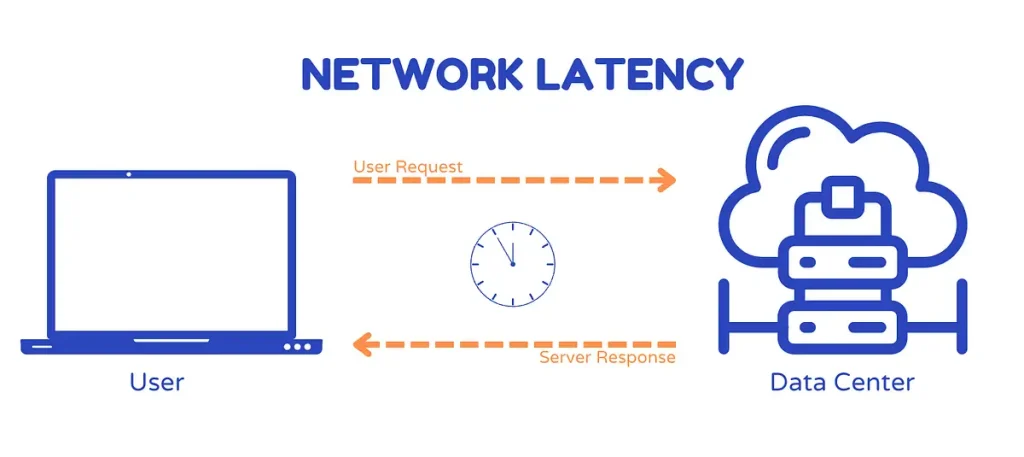
What is Latency?
Latency refers to the time delay it takes for data to travel between two points on a network. Essentially, it’s the time it takes for a signal to go from your device to a server and back again, typically measured in milliseconds (ms). The lower the latency, the faster this round-trip happens, resulting in more responsive online interactions.
For example, when you click on a webpage, latency is the time it takes for the server to receive your request and send the information back to display on your screen. In contrast to download and upload speeds, which measure how fast data is transferred, latency measures how fast it begins.
If you’re curious about your own internet latency, you can easily check it using tools like speedtest.net or Fast.com, which will provide a detailed report on your connection’s latency in real-time.
What Causes High Latency?
Numerous factors can contribute to higher latency, slowing down the response time between your device and the internet. These include:
1. Geographical Distance
One of the biggest factors affecting latency is the physical distance between your device and the server you’re communicating with. The farther the data has to travel, the longer it will take, even though the data itself is moving at the speed of light. For example, data traveling between continents typically experiences more latency than data transmitted within the same city.
To check how distance impacts your own internet connection, you can use tools like speed.cloudflare.com, which offers insights on latency, as well as download and upload speeds across various server locations.
2. Network Traffic and Congestion
When many people use the internet at the same time, especially in densely populated areas, the sheer volume of data traffic can overwhelm networks. As a result, this congestion can lead to slower data transmission times.
3. Network Infrastructure and Hardware
The route your data takes is not always direct. It often passes through multiple network devices such as routers and switches before reaching its destination. Each stop along this path can add small delays that accumulate, increasing the overall latency.
4. Device and Software Issues
Old or inefficient hardware, such as outdated routers or overloaded servers, can introduce delays. Similarly, applications or processes running in the background, such as large file downloads or system updates, can clog bandwidth and increase latency.
Effects of High Latency
High latency affects various online experiences in different ways, often leading to noticeable lags or delays. Some areas where latency can have a significant impact include:
1. Online Gaming
In multiplayer video games, even a few milliseconds of delay can cause gameplay issues, such as lag, delayed inputs, or unsynchronized player movements. This can make a big difference in competitive games where fast reactions are critical.
2. Video Calls and Conferencing
For platforms like Zoom or Skype, low latency is essential for smooth conversations. High latency can cause delays in audio and video, resulting in awkward conversations where participants speak over each other due to delayed transmission.
3. Streaming
When watching movies or videos online, high latency may cause buffering, lower the video quality, or delay the start of playback, leading to a frustrating viewing experience.
4. VoIP Services
Similar to video conferencing, Voice over IP (VoIP) calls rely on low latency for clear, uninterrupted communication. High latency can cause echoes, voice delays, or overlapping conversations, reducing the quality of the call.
5. Cloud-Based Workflows
When using cloud applications like Google Drive, Office 365, or other collaborative tools, high latency can slow down the synchronization of documents, making real-time collaboration sluggish and inefficient.
Solutions for Lowering Latency
While latency cannot be eliminated entirely, several solutions exist to reduce it and improve internet performance. Depending on the cause, these fixes can range from simple adjustments to more technical optimizations:
1. Upgrade Your Internet Package
If your connection consistently experiences high latency, you might want to upgrade to a faster plan with more bandwidth. This can help improve overall internet performance, especially in households with many connected devices.
2. Switch to Wired Ethernet Connections
Wireless networks tend to introduce higher latency than wired ones due to interference and signal loss. Using an Ethernet cable can provide a more stable and faster connection, which reduces latency for tasks like gaming, streaming, or remote work.
3. Optimize Your Network Equipment
Ensure your modem and router are up to date and optimized for modern speeds. Outdated or low-quality equipment can bottleneck your connection, increasing latency. Positioning your router in a central location and avoiding interference from other electronic devices can also help improve wireless performance.
4. Reduce Background Processes
Many applications and devices connected to your network can consume bandwidth even when not in active use. Shutting down unnecessary background tasks, pausing large downloads, or disconnecting unused devices can free up bandwidth and reduce latency.
5. Use a Fast DNS Server
The Domain Name System (DNS) is responsible for translating website names into IP addresses. Using a faster DNS server, such as Google Public DNS or Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1, can reduce the time it takes to connect to websites, which in turn can help lower latency.
6. Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
Some routers come with QoS settings that allow you to prioritize certain types of traffic, such as gaming or video calls, over other activities like downloading or streaming. This can help ensure that latency-sensitive tasks receive the bandwidth they need.
7. Monitor and Diagnose Your Network
Using tools like Fast.com or SpeedTest.net can help you pinpoint the cause of latency issues on your network, allowing you to target specific fixes.
How Starlink Lowers Latency in Satellite Internet
Historically, satellite internet latency has been notoriously high due to the long distances signals must travel between satellites and Earth. However, Starlink has revolutionized this by using Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites that orbit at just 550 km above the Earth. This drastically reduces the travel distance for data, significantly lowering satellite internet latency compared to traditional systems.
Starlink’s latency can range from 20-50 ms, making it competitive with traditional wired connections and a viable option for people in rural or underserved areas where fiber or cable broadband is unavailable. With its ongoing expansion, Starlink is continuously working to further reduce latency and improve performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is considered high latency?
Latency over 100 ms is generally considered high for tasks like gaming, video calls, or streaming. Ideally, you want latency to be under 50 ms for the best experience.
2. How does Starlink’s latency compare to traditional satellite internet?
Traditional satellite internet can have latency of around 600 ms or higher, while Starlink offers much lower latency, between 20-50 ms, thanks to its LEO satellite network.
3. Can network congestion cause latency issues?
Yes, high traffic on a network can slow down data transmission, increasing latency, especially during peak usage times.
4. Does faster internet speed reduce latency?
Faster speeds can help alleviate bandwidth issues, but latency is more influenced by distance, congestion, and the quality of the network infrastructure than by speed alone.
5. How can I check my internet latency?
You can use tools like speedtest.net or PingPlotter to measure your internet latency. These tools show the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a server and back.
Addressing latency issues is key to improving your internet experience, whether you’re gaming, streaming, or working from home. Although some latency is inevitable, by understanding the causes and implementing the right solutions—such as upgrading hardware, switching to wired connections, or using Starlink’s low-latency satellite internet—you can significantly reduce delays and enjoy a smoother, more responsive connection.


